Collecting social security is an intricate, but necessary part of retirement. The funds provide retired individuals with a steady income after their working days are over. However, the timing and regulations behind social security can be frustrating. The rules are plentiful and the explanations are not always clear. The United States Social Security Administration examines your age, current place of employment (if there is one), and family situation before dictating the level of your benefit. Read on for some of the basic and important topics to consider before applying for social security. Use the information in this article as a resource to select the optimal time to begin collecting benefits.
Collecting social security is an intricate, but necessary part of retirement. The funds provide retired individuals with a steady income after their working days are over. However, the timing and regulations behind social security can be frustrating. The rules are plentiful and the explanations are not always clear. The United States Social Security Administration examines your age, current place of employment (if there is one), and family situation before dictating the level of your benefit. Read on for some of the basic and important topics to consider before applying for social security. Use the information in this article as a resource to select the optimal time to begin collecting benefits.
Effects of Age on Your Social Security
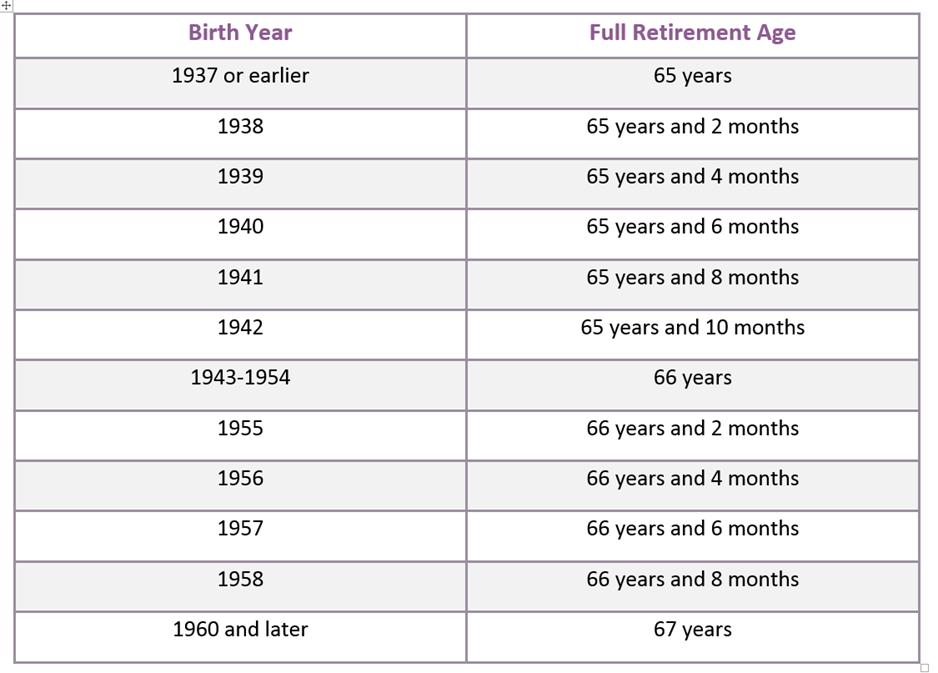
To become eligible for social security benefits the government requires that you work at least 10 years to earn the minimum 40 credits. Once you are eligible timing becomes the hardest part of deciding when to receive. The United States Social Security Administration bases the benefit off the full retirement age. The full retirement age is the age at which a person may first become entitled to full or unreduced retirement benefits. This age changes depending on when you were born. Use the chart depicted below to search for your birth year in the left-hand column and then move to the right-hand column to find your full retirement age.
At What Age Should You Start Collecting Social Security?
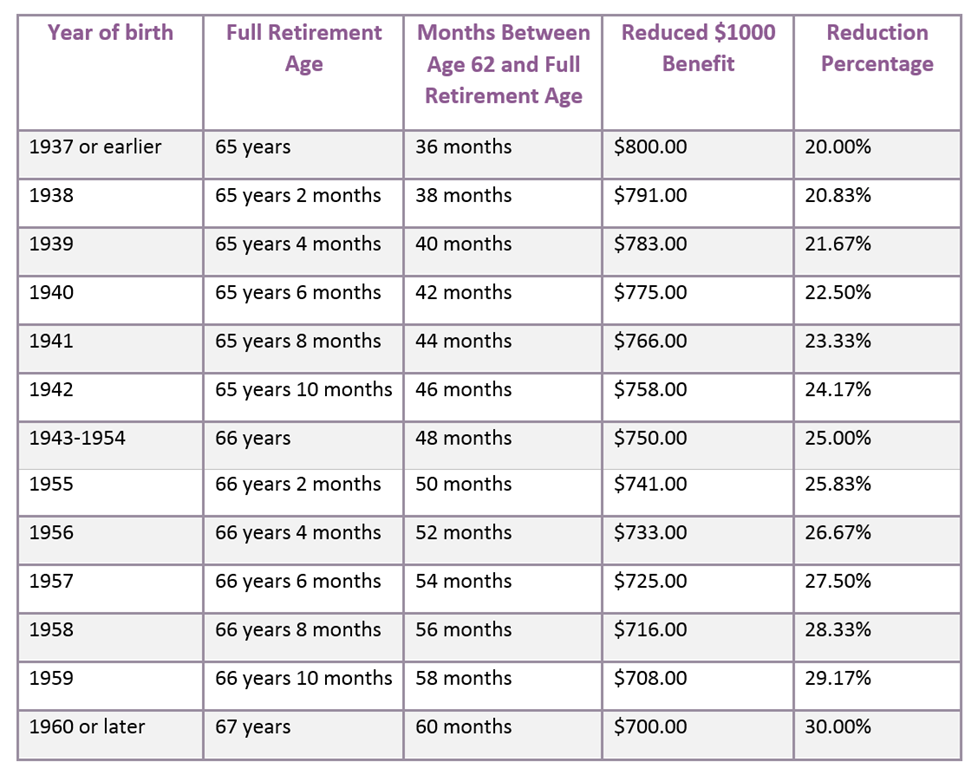
If you apply for benefits at your full retirement age, you will receive the maximum amount possible. But any earlier application will receive deductions on the full benefit. The earliest you can apply for social security is age 62, but that age will also see the most substantial reductions. For example, consider an individual with a full retirement age of 67. This individual can apply to receive benefits at age 62, but there will be reductions because the benefits will be provided for a longer time than someone applying at the full retirement age. However, if this person waits until age 67, then there would not be any reductions. The closer you are to your full retirement age when you apply, the less substantial the reductions on the benefits are. The chart below shows the reduction on social security for someone applying at the age of 62. Find your birth year in the left-hand column and trace across that row to discover what a $1000 benefit would be reduced to. The reduction percentage of the benefits vary, but they are smaller the closer you are to the full retirement age.
How to Apply for and Start Collecting Social Security
Now that you know at what age you can apply, it's time to cover the application process. There are three different ways that a person can apply for social security – by phone, in person, or online. Regardless of what method you choose, you will need to supply personal information like your social security number, your bank/financial institution account number and routing number, your date of birth (including your birth certificate), your citizenship status, and when you would like your social security benefits to start. You will also need to provide work information, including copies of your most recent W-2s, the name and address of your employer, and more information.
To apply for social security benefits online visit https://www.ssa.gov/. Or you can apply by phone: 1-800-772-1213.
Working While Receiving Benefits
 Maintaining a job while receiving benefits creates another set of restrictions on collecting social security. You can apply for social security, receive the benefits, and maintain your current job or part time position. Even though that supplies you with two resources for income there is a set of limitations. If you are under the full retirement age for the entire year you are working and receiving social security, then $1.00 will be deducted from your benefit payment for every $2.00 you earn above the annual limit of $16,920. If you will be reaching your full retirement age within the year you are working and receiving social security benefits, then $1.00 will be deducted for every $3.00 above the annual limit of $44,880. Once you reach your full retirement age your earnings through social security will not be reduced no matter how much you earn at a full or part time job. It is important to fully understand these limits especially if you are applying for social security while working under the full retirement age. Depending on your annual salary you can drastically alter the amount of your benefit.
Maintaining a job while receiving benefits creates another set of restrictions on collecting social security. You can apply for social security, receive the benefits, and maintain your current job or part time position. Even though that supplies you with two resources for income there is a set of limitations. If you are under the full retirement age for the entire year you are working and receiving social security, then $1.00 will be deducted from your benefit payment for every $2.00 you earn above the annual limit of $16,920. If you will be reaching your full retirement age within the year you are working and receiving social security benefits, then $1.00 will be deducted for every $3.00 above the annual limit of $44,880. Once you reach your full retirement age your earnings through social security will not be reduced no matter how much you earn at a full or part time job. It is important to fully understand these limits especially if you are applying for social security while working under the full retirement age. Depending on your annual salary you can drastically alter the amount of your benefit.
Family Members Receiving Benefits
Once you decide to apply and receive social security other family members may qualify to receive benefits. There are benefit plans for your spouse, ex-spouse, and children, but there are requirements that must be met. Should all the requirements be met the entitled individual can get up to one-half of the full retirement benefit amount and money will not be deducted from your personal statement. Below is a list of the people that qualify for assistance and the requirements that must be met.
1. Spouse
- Benefit spouse is entitled to receive based on their work is less than the benefit they would receive partnered with your work. Still qualify even if they never worked.
- Must be at least 62 years of age.
2. Ex-Spouse
- Benefit ex-spouse is entitled to receive based on their work is less than the benefit they would receive partnered with your work. Still qualify even if they never worked.
- Must be at least 62 years of age.
- Marriage lasted 10 years or longer.
- Must remain unmarried.
There are several other situations to note when it comes to ex-spouses receiving benefits:
- If you qualify for benefits but do not apply for them your ex-spouse can receive their benefits on your accord if you have been divorced for at least two years.
- If your ex-spouse is eligible for retirement benefits but the benefits on your account are higher than your ex-spouse can receive an additional amount that equals the higher amount without going over.
- If your ex-spouse continues to work while receiving benefits the same limits that were mentioned above that apply to you apply to them.
- Finally, if your ex-spouse will receive a pension based on work the amount they receive can be altered.
3. Children
- Must be unmarried.
- Can be either A) under the age of 18. B) between 18-19 years old and a full-time student in high school. C) 18 or older and disabled from a disability that started before age 22.
- Unless the child is disabled they will receive benefits until high school graduation or 2 months after turning 19.
- Disabled children can continue to receive benefits past the age of 19.
When Should I Apply for Social Security
 There is no perfect time to apply for social security benefits. The best advice is to think hard about your current situation mixed with the information above. The timing of your application changes how much money you receive and how long you receive it. If you apply early the benefit is reduced, but there are more payments. If you apply once you reach your full retirement age there is a larger benefit, but you are receiving it for a shorter time. It is a difficult decision and should be discussed closely with friends and family members. Here is another list of questions to consider while you are going through the decision-making process.
There is no perfect time to apply for social security benefits. The best advice is to think hard about your current situation mixed with the information above. The timing of your application changes how much money you receive and how long you receive it. If you apply early the benefit is reduced, but there are more payments. If you apply once you reach your full retirement age there is a larger benefit, but you are receiving it for a shorter time. It is a difficult decision and should be discussed closely with friends and family members. Here is another list of questions to consider while you are going through the decision-making process.
- Are you still working? How much do you make? Will there be reductions to your benefit if you are still working under your full retirement age?
- What is your family situation? Is there anyone within your family that may benefit greatly by receiving the rewards that come with your benefit?
- How is your current health? Do you struggle with health and are under the full retirement age? If so you may want to consider retiring and apply for social security even though you are not at the full retirement age.
- What is your family history with health? Are people living long lives? If so you may have good family health history and wait for the full retirement age to start receiving benefits.
Ultimately the choice is yours after you've weighed the options, but at least you're one step closer to understanding the conditions!
Citations:
"Social Security Benefits." The United States Social Security Administration. The United States Social Security Administration, Web. 24 May 2017.